- 모듈(Module)
필요한 함수나 변수, 클래스를 모아 놓은 스크립트 파일(.py)

EX) factorial 구하기
def factorial(n):
result = 1
for i in range(1,n+1):
result *= i
return result
print('5! =',factorial(5))import math
print('5! =', math.factorial(5))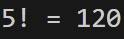
- 모듈 안에서 특정 함수만 불러오기

EX)
from math import factorial
print('5! =',factorial(5))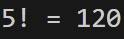
* "모듈이름"까지 사용하면 ERROR
from math import factorial
print('5! = ',math.factorial(5))
-동시에 여러 함수 불러올 수 있다.
EX)
from math import pow, sqrt
a = pow(2,3) #pow(): 제곱수
b = sqrt(4) #sqrt(): 제곱근(루트)
print(a)
print(b)
=> 부동 소수형으로 출력된다.
- 모듈 안에서 특정 함수만 불러오기

모듈 이름없이 함수나 변수를 직접 사용
*(asterisk)기호는 정규 표현식으로 모든것이란 뜻
EX)
from math import *
print(pi)
print(factorial(5))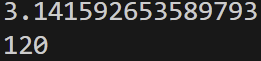
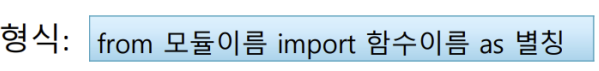
- 모듈/함수 이름에 별명 붙이기
1. 모듈이름에 별칭사용

2. 모듈 안의 함수 이름에 별칭사용
EX)
import math as m
a = m.pow(2,3)
b = m.sqrt(4)
print(a)
print(b)from math import pow as p, sqrt as s
a = p(2,3)
b = s(4)
print(a)
print(b)
- 모듈을 해제(del)
EX)
import math
a = math.pow(2,3)
print(a)
del math
a = math.pow(2,3)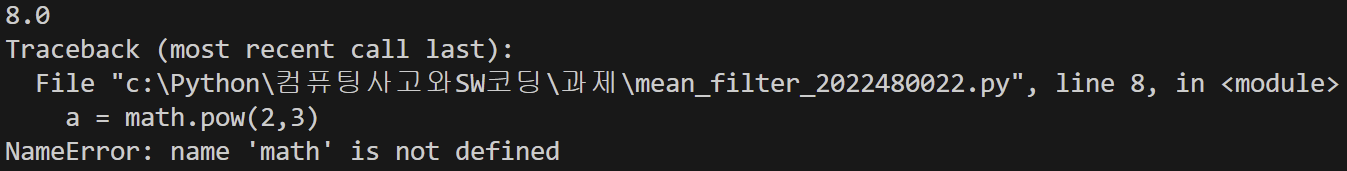
=> del math로 지우면 ERROR
- 사용자 정의 모듈
- my_mod.py
pi = 3.141592
def add(a,b):
return a+b
def sub(a,b):
return a-b- main.py
import my_mod
a = my_mod.add(5,3)
b = my_mod.sub(5,3)
print(a)
print(b)
print(my_mod.pi)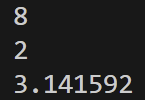
- ★ __name__변수 ★
- my_mod.py
pi = 3.141592
def add(a,b):
return a+b
def sub(a,b):
return a-b
print("*** main.py에서는 보이면 안되는 부분 ***")=> 다음과 같이 수정하고 main.py를 실행하면

모듈 import할때 모듈 안의 실행하는 부분도 동작한다.
이것을 막는 때 사용하는 것이 __name__변수 (내부적으로 사용되는 특별한 함수)
- 자기 스크립트가 실행 중
__name__ 변수 => "__main__"라는 값이 들어감
- 모듈이 실행되고 있으면
__name__변수 => 모듈의 이름이 들어감
EX)
- my_mod.py
pi = 3.141592
def add(a,b):
return a+b
def sub(a,b):
return a-b
if __name__ == "__main__":
print("*** main.py에서는 보이면 안되는 부분 ***")
else:
print(__name__)=> 다음과 같이 수정하고 main.py를 실행하면
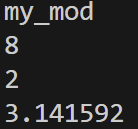
my__mod.py의 __name__변수에 값이 my_mod가 되면서 불필요한 부분없이 main.py실행
표준모듈
- random모듈
임의의 수(난수)를 생성하거나 리스트 내의 요소를 무작위로 선택 또는 섞는 함수 포함
- randint(start, stop)
start~end사이 랜덤 정수 반환
import random
print(random.randint(1,6))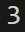
- random()
0~1.0 사이의 랜덤 실수를 반환
import random
print(random.random())
- choice(list)
리스트 항목을 랜덤하게 반환
import random
color = ['red','green','blue']
print(random.choice(color))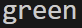
- shuffle(list)
리스트 항목을 랜덤하게 섞음
import random
color = ['red','green','blue']
random.shuffle(color)
print(color)
- OS모듈(operating system)
파이썬이 실행되는 운영체제와 관계없이 운영체제의 기본적인 기능을 다룰 수 있도록 해주는 모듈
- listdir()
현재 경로의 파일과 디렉토리 리스트 반환
import os
print(os.listdir())
- mkdir('디렉토리_이름')
새로운 디렉토리 생성
import os
os.mkdir("TEST")
print(os.listdir())
=>TEST항목이 추가됨
- getcwd()
현재 경로를 return
- chdir("../")
현재 경로를 상위 경로로 변경(다른 경로도 가능)
*절대경로: 최상위 디스크부터 시작

*상대경로: 현재 작업 디렉터리부터 시작

- time모듈
- time()
기준 시간 이후 경과한 시간을 초 단위 반환 (float값이 반환)
import time
t = time.time()
print(t)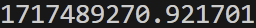
- localtime(경과한 초)
현재 지역의 시간대 출력 (struct_time: 객체에 정보를 넣어서 돌려줌)
import time
t = time.time()
time_local = time.localtime(t)
print(time_local)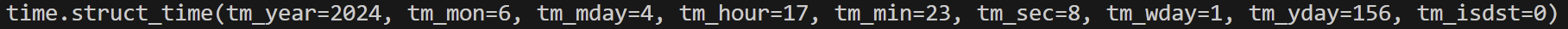
- strtftime(시간객체)
tima.localtime이 만든 시간 객체를 원하는 포맷으로 출력
import time
t = time.time()
time_local = time.localtime(t)
print(time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d', time_local))
print(time.strftime('%d', time_local))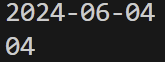
%d : 일 / %m : 숫자 월 / %Y : 네 자릿수 연도
%c : 날짜, 요일, 시간을 출력, 현재 시간대 기준
- sleep
해당 초 만큼 시간을 지연하는 함수
import time
time.sleep(3)
print("3초지남")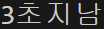
=>3초가 지난뒤 출력됨
EX) 피보나치 수열 알고리즘 동작 시간 측정
import time
def fib(n):
a,b = 0,1
while b<n:
print(b,end=' ')
a,b = b,a+b
print()
start = time.time()
fib(10000)
end = time.time()
print(end-start)
=> 실행하는 컴퓨터에 따라 시간은 다르다.
- datatime 모듈
날짜와 시간에 관련된 모듈, datatime모듈 안에 datatime클래스를 사용
- datatime.today()
현재의 날짜와 시간을 반환
import datetime
print(datetime.datetime.today())
EX) 제대 날짜를 계산(특정 날짜와 시간으로 객체를 만들 수 있다)
import datetime
today = datetime.datetime.today()
end_day = datetime.datetime(2024,9,30)
d_day = end_day - today
print(d_day)
- calendar모듈
달력 기능을 제공
import calendar
cal = calendar.month(2024,1)
print(cal)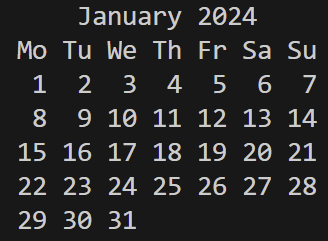
써드 파티(3rd Party)모듈
외부 회사나 단체가 제공하는 모듈
- Numpy
파이썬의 고성능 과학 계산용 패키지

EX)
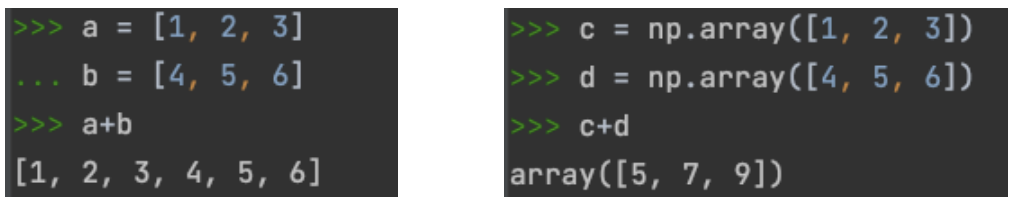
- 2차원 배열은 matrix와 같이 생성
a = np.array([1,2,3])
b = np.array([[1,2,3],[4,5,6]])- shape : 크기확인 / size : element수
np.shape(b)
np.size(b)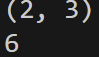
- arange([start,],stop,[step,])
>>> np.arange(10)
array([0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9])
>>> np.arange(2,10,2)
array([2,4,6,8])- linespace(start,stop,num=50)
>>> np.linespace(1,2,3)
array([1. , 1.5, 2. ])
>>> np.linespace(1,3,3)
array([1., 2., 3.])
Practice
import numpy as np
v1 = np.array([1,2,3])
v2 = np.array([4,5,6])
v3 = np.array([7,8])
print(v1+v2)
print(v1*3)
print(v1+v3) #ERROR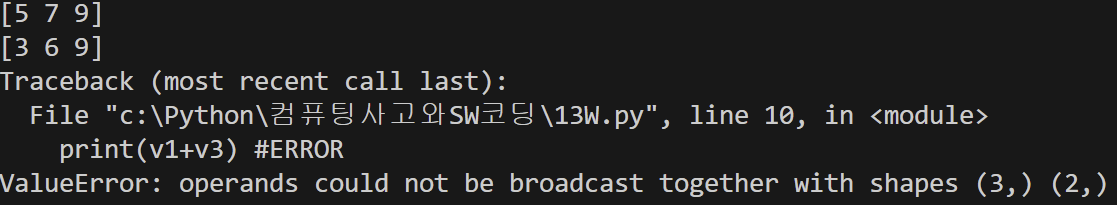
import numpy as np
m1 = np.array([[1,2],[3,4]])
m2 = np.array([[5,6],[7,8]])
print(m1+m2)
print(m2//m1)
print(m1*m2) #요소 곱
print(m1@m2) #행렬 곱
print(m1.T) #전치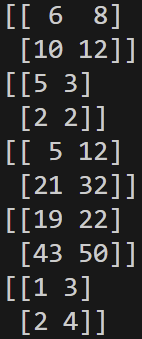
import numpy as np
v4 = np.arange(1,10)
m3 = np.reshape(v4,(3,3))
s1 = m3[1,1]
m4 = m3[0:1]
v5 = m3[0,:]
print(v4)
print(m3)
print(s1)
print(m4)
print(v5)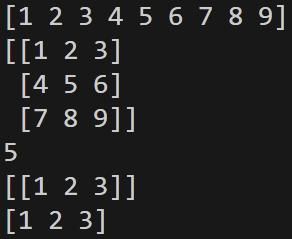
import numpy as np
v4 = np.arange(1,10)
m3 = np.reshape(v4,(3,3))
m5 = np.reshape(v4[1:], (2,4))
m6 = np.zeros_like(m3)
m7 = np.ones_like(m5)
m8 = np.reshape(v4[1:],(4,-1))
print(v4)
print(m3)
print(m5)
print(m6)
print(m7)
print(m8)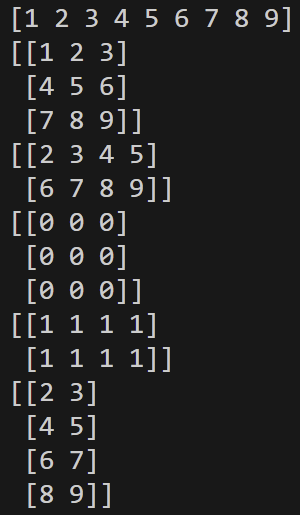
- ★np.where★
np.where(조건, 결과, else결과)
>>> a = np.arange(10)
>>> np.where(a<5,a,a*10)
array([0,1,2,3,4,50,60,70,80,90])>>> a = np.arange(0, 100, 10)
>>> a
array([0,10,20,30,40,50,60,70,80,90])
>>> np.where(a%20==0)
(array([0,2,4,6,8]),) #인덱스
>>> a[np.where(a%20==0)]
array([0,20,40,60,80])
- np.zeros() / np.ones()
np.zeros(): 0으로 채워진 배열 생성
np.ones(): 1로 채워진 배열 생성
>>> np.zeros(shape=(3,5))
array([[0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 0., 0.]])
>>> np.ones(shape=(2,3))
array([[1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1.]])
- full() / eye()
np.full(shape, fill_value): 지정한 값(fill_value)으로 채워진 배열 생성
np.eye(N): identicla matrix생성, 대각 방향으로 1로 세워진 행렬
>>> np.full(shape=(3,3), fill_value=5)
array([[5, 5, 5],
[5, 5, 5],
[5, 5, 5]])
>>> np.eye(N=3)
array([[1., 0., 0.],
[0., 1., 0.],
[0., 0., 1.]])- pad()
array의 특정 축 방향으로 padding 수행
>>> A=np.ones((2,2))
>>> A
array([[1., 1.],
[1., 1.]])
>>> np.pad(A,((1,2),(0,1)),'constant',constant_values=2)
array([[2., 2., 2.],
[1., 1., 2.],
[1., 1., 2.],
[2., 2., 2.],
[2., 2., 2.]])
>>> np.pad(A,(1,2),'constant',constant_values=0)
array([[0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 1., 1., 0., 0.],
[0., 1., 1., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 0., 0.]])행의 시작에 1만큼 pad / 행의 끝에 2만큼 pad
열의 시작에 0만큼 pad / 열의 끝에 1만큼 pad
행의 시작에 1만큼 pad / 행의 끝에 2만큼 pad
열의 시작에 1만큼 pad / 열의 끝에 2만큼 pad
'3-1 > Python' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 14주차-Exception (0) | 2024.06.11 |
|---|---|
| 12주차-Class (0) | 2024.05.31 |
| 11주차-file read/ write (0) | 2024.05.17 |
| 10주차-Dictionary and Set (0) | 2024.05.12 |
| 9주차-Function (0) | 2024.05.12 |